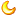吴哥古蹟,又名吴哥考古园,位於東南亞中南半島的柬埔寨西北方暹粒省,吳哥(Angkor)是高棉語「城市」的意思。古蹟群分布在400平方公里的范围内,包括高棉王國从9世纪到15世纪历代都城和寺庙,如吴哥窟、吳哥城、巴戎寺、女王宫等遗蹟。聯合國教科文組織於1992年將吳哥古蹟列為世界文化遗产。
$ R4 k4 p$ R0 C4 Cos.tvboxnow.com2007年國際研究團隊發現在吳哥王朝鼎盛時期,吳哥地區面積近3,000平方公里,是工業革命前全球面積最大的城市。當時吳哥擁有50至100萬人口,為供應足夠糧食以及調節旱季與雨季,吳哥地區建立了一套精密灌溉系統,以完善的水渠與眾多的儲水用人工湖來發展農業。
$ S- W* W* b% Z& g4 wos.tvboxnow.comTVBNOW 含有熱門話題,最新最快電視,軟體,遊戲,電影,動漫及日常生活及興趣交流等資訊。 `) e, M+ v' S& s0 W8 E
Angkor (Khmer: អង្គរ, "Capital City") is a region of Cambodia that served as the seat of the Khmer Empire, which flourished from approximately the 9th to 15th centuries. The word Angkor is derived from the Sanskrit nagara (नगर), meaning "city". The Angkorian period began in AD 802, when the Khmer Hindu monarch Jayavarman II declared himself a "universal monarch" and "god-king", until 1351, when Angkor first fell under Ayutthayan suzerainty, to 1431, when Ayutthaya put down a rebellion and sacked the Khmer capital, causing its population to migrate south to Longvek.TVBNOW 含有熱門話題,最新最快電視,軟體,遊戲,電影,動漫及日常生活及興趣交流等資訊。& a9 x! D/ z% k, x# ?
The ruins of Angkor are located amid forests and farmland to the north of the Great Lake (Tonlé Sap) and south of the Kulen Hills, near modern-day Siem Reap city (13°24′N, 103°51′E), in Siem Reap Province. The temples of the Angkor area number over one thousand, ranging in scale from nondescript piles of brick rubble scattered through rice fields to the magnificent Angkor Wat, said to be the world's largest single religious monument. Many of the temples at Angkor have been restored, and together, they comprise the most significant site of Khmer architecture. Visitor numbers approach two million annually, and the entire expanse, including Angkor Wat and Angkor Thom is collectively protected as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. This popularity of the site among tourists presents multiple challenges to the preservation of the ruins.
: r7 m% a7 B( e* g9 iIn 2007, an international team of researchers using satellite photographs and other modern techniques concluded that Angkor had been the largest preindustrial city in the world, with an elaborate system of infrastructure connecting an urban sprawl of at least 1,000 square kilometres (390 sq mi) to the well-known temples at its core. The closest rival to Angkor, the Mayan city of Tikal in Guatemala, was between 100 and 150 square kilometres (39 and 58 sq mi) in total size. Although its population remains a topic of research and debate, newly identified agricultural systems in the Angkor area may have supported up to one million people. |